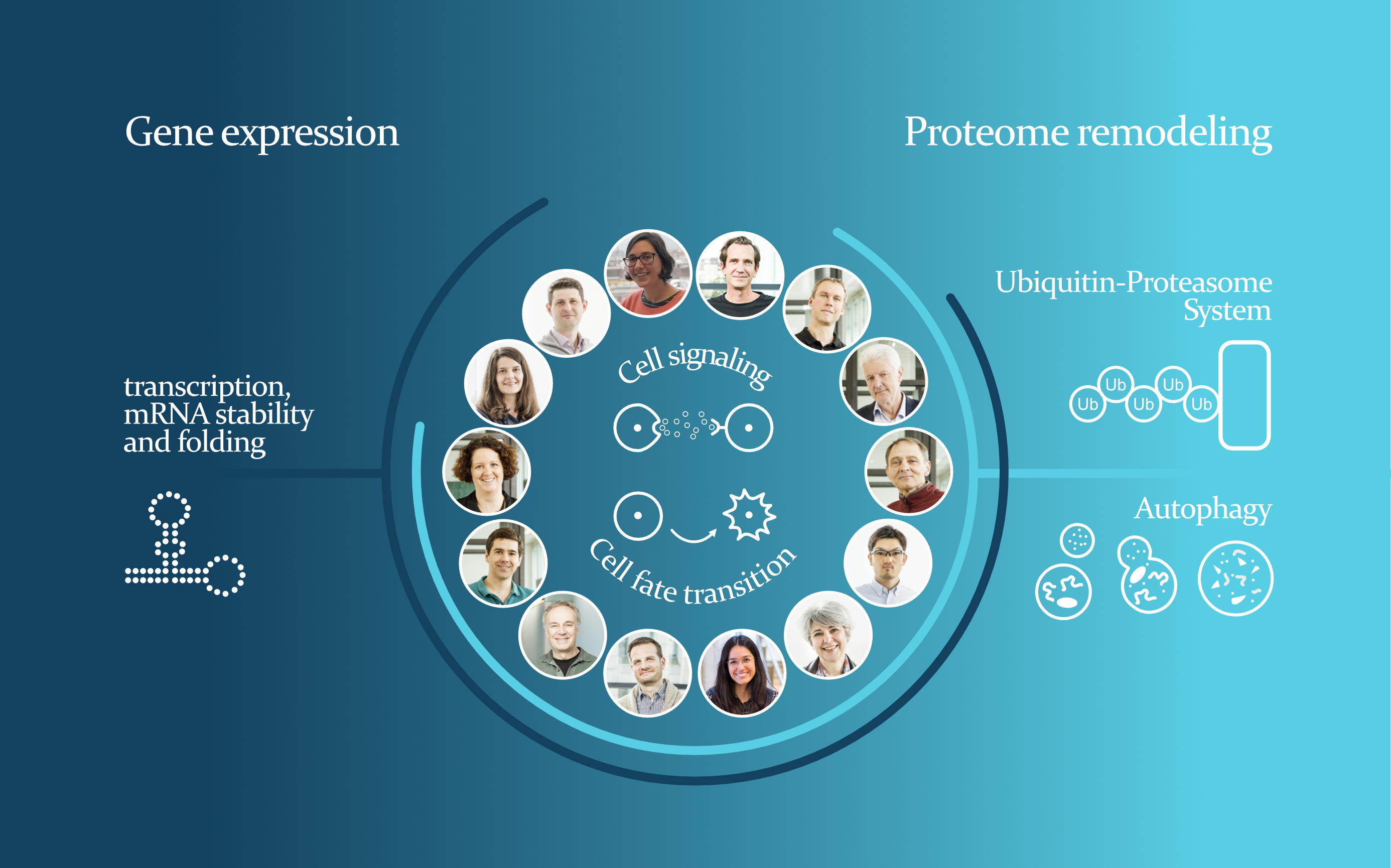
Homeostasis can be described as the effort of an organism to maintain a state of inner balance despite external changes in its environment. This inner balance is necessary to preserves cell function and survival, and it is maintained by molecules that interpret the signals received by the environment and translate them into the correct output. But life is dynamic, and cells need to differentiate or respond to stress. During cell fate changes, homeostasis needs to be broken and a new state needs to be established, which the new cell will again seek to maintain for as long as it is appropriate.
Perturbations in homeostasis have been linked to developmental disorders, muscular dystrophy, premature aging, neurodegeneration, and cancer.